
Have you ever wanted to monitor who’s logging into your computer and when? On Professional editions of Windows, you can enable logon auditing to have Windows track which user accounts log in and when.
The Audit logon events setting tracks both local logins and network logins. Each logon event specifies the user account that logged on and the time the login took place. You can also see when users logged off.
Enable Logon Auditing
First, open the local group policy editor – press the Windows key, type gpedit.msc in the Start menu, and press Enter. (You can also enable logon event auditing on a domain controller if you administer a network with centralized logins.)

Navigate to the following folder: Local Computer Policy –> Computer Configuration –> Windows Settings –> Security Settings –> Local Policies –> Audit Policy.

Double-click the Audit logon events policy setting in the right pane to adjust its options. In the properties window, enable the Success checkbox to log successful logons. You can also enable the Failure checkbox to log failed logins.

Viewing Logon Events
After enabling this setting, Windows will log logon events – including a username and time – to the system security log.
To view these events, open the Event Viewer – press the Windows key, type Event Viewer, and press Enter to open it.

Navigate to the Windows Logs –> Security category in the event viewer.
Look for events with event ID 4624 – these represent successful login events.

To see more information – such as the user account that logged into the computer – you can double-click the event and scroll down in the text box. (You can also scroll down in the text box underneath the list of events.)

If your security log is cluttered, you can click the Filter Current Log option in the sidebar and filter by event ID 4624. The Event Viewer will display only logon events.
Because this is just another event in the Windows event log with a specific event ID, you can also use the Task Scheduler to take action when a logon occurs. You can even have Windows email you when someone logs on.












 An application server functions the same as a computer that executes the commands requested by the Web server inorder to fetch the data from the databases. It transfers the applications from one device to another. It is a generalized software engine, which implements the execution of the application server in order to create the applications for different devices. The transferring function is not concerned with the type of application functions. The application server executes the assigned specific instances in the exact procedure and step wise approach of the programs, routines and scripts by supporting their applied applications.
An application server functions the same as a computer that executes the commands requested by the Web server inorder to fetch the data from the databases. It transfers the applications from one device to another. It is a generalized software engine, which implements the execution of the application server in order to create the applications for different devices. The transferring function is not concerned with the type of application functions. The application server executes the assigned specific instances in the exact procedure and step wise approach of the programs, routines and scripts by supporting their applied applications. A Web server can be a software (in the form of an application program) or hardware (in the form of a computer). Its basic function is to accept the HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) requests from the client side, then process and serve them back as the HTTP response along with the optional data content. The responses sent are in the form of HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) web pages or documents. The basic function of the Web server is to transfer the web content, which are accessed through the internet to the respective Clients.
A Web server can be a software (in the form of an application program) or hardware (in the form of a computer). Its basic function is to accept the HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) requests from the client side, then process and serve them back as the HTTP response along with the optional data content. The responses sent are in the form of HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) web pages or documents. The basic function of the Web server is to transfer the web content, which are accessed through the internet to the respective Clients.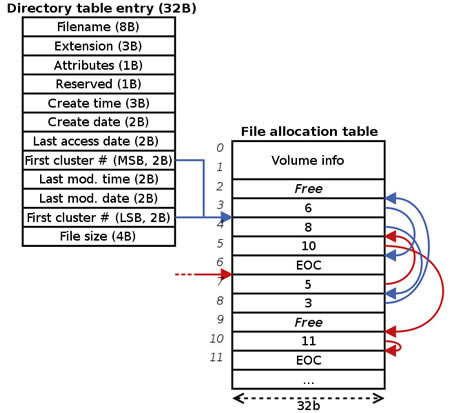 FAT32 is a version of the File Allocation Table which is available in the Windows 95 OSR 2 and Windows 98 operating systems. It is the common file system which is used in most the computers. The file system obtained its name from the fact that it uses a table of 32-bit storage. Its basic function is to record the disk addresses of each file during the partition. The file system can have up to 24 partitions, which may range from 32MB to 137GB. These partitions operates under the Windows 9x operating system, and they are responsible to available the space on the hard disk. There are limitations of the Windows9x operating system, which are to be considered while making the partitions available. All the remaining operating systems use the FAT32 file system as per their accordance and capability. The FAT32 file system is typically used as a means of file storage in a Windows 9x computer, on a partition not exceeding 126GB.
FAT32 is a version of the File Allocation Table which is available in the Windows 95 OSR 2 and Windows 98 operating systems. It is the common file system which is used in most the computers. The file system obtained its name from the fact that it uses a table of 32-bit storage. Its basic function is to record the disk addresses of each file during the partition. The file system can have up to 24 partitions, which may range from 32MB to 137GB. These partitions operates under the Windows 9x operating system, and they are responsible to available the space on the hard disk. There are limitations of the Windows9x operating system, which are to be considered while making the partitions available. All the remaining operating systems use the FAT32 file system as per their accordance and capability. The FAT32 file system is typically used as a means of file storage in a Windows 9x computer, on a partition not exceeding 126GB. NTFS is an advanced and featured rich file systems. The acronym NTFS stands for, New Technology File System. This file system is the most advanced and latest file system, which has a highly advanced writing techniques, improved security and high capability of space utilization. The hard disk when formatted is divided into partitions or major divisions. Within every partition, the operating system keeps track of all the files, which are stored by that respective OS (Operating System). Hence, each file is now stored on a hard disk in one or more cluster or group format, which ranges from 512 byte to 64 bytes. The files are recorded into a special file format in NTFS, these file format are known as Master File Table (MFT). These records are further used to locate the files if scattered among the clusters. NTFS also tries to find the contiguous storage space, which holds the entire file along with its clusters.
NTFS is an advanced and featured rich file systems. The acronym NTFS stands for, New Technology File System. This file system is the most advanced and latest file system, which has a highly advanced writing techniques, improved security and high capability of space utilization. The hard disk when formatted is divided into partitions or major divisions. Within every partition, the operating system keeps track of all the files, which are stored by that respective OS (Operating System). Hence, each file is now stored on a hard disk in one or more cluster or group format, which ranges from 512 byte to 64 bytes. The files are recorded into a special file format in NTFS, these file format are known as Master File Table (MFT). These records are further used to locate the files if scattered among the clusters. NTFS also tries to find the contiguous storage space, which holds the entire file along with its clusters. Domains and workgroups are two different methods for organizing computers in a network. The main difference between the two is in the manner they operate, chiefly how the computers and other resources on the networks are managed.
Domains and workgroups are two different methods for organizing computers in a network. The main difference between the two is in the manner they operate, chiefly how the computers and other resources on the networks are managed. Advantages of Domain over workgroup:
Advantages of Domain over workgroup:



































